1.fastjson简介
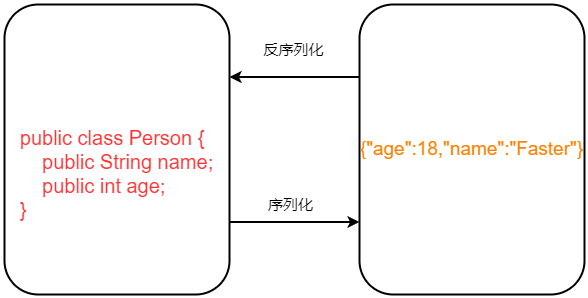
fastjson 是阿里巴巴开发的 java语言编写的高性能 JSON 库,用于将数据在 Json 和 Java Object之间相互转换。它没有用java的序列化机制,而是自定义了一套序列化机制。
主要提供两个接口方法:
1
2
3
4
| //序列化:一个
JSON.toJSONString
//反序列化:二个
JSON.parseObject/JSON.parse
|
1.1 简单示例
注意
只有符合Java Bean格式的对象才能Fastjson被转为JSON
创建一个Person类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class Person {
public String name;
public int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
|
ParseObject与Parse使用对比
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个Java Bean对象
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("106");
person.setAge(18);
System.out.println("--------------序列化-------------");
//将其序列化为JSON
String JSON_Serialize = JSON.toJSONString(person);
System.out.println(JSON_Serialize);
System.out.println("-------------反序列化-------------");
//使用parse方法,将JSON反序列化为一个JSONObject
Object o1 = JSON.parse(JSON_Serialize);
System.out.println(o1.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(o1);
System.out.println("-------------反序列化-------------");
//使用parseObject方法,将JSON反序列化为一个JSONObject
Object o2 = JSON.parseObject(JSON_Serialize);
System.out.println(o2.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(o2);
System.out.println("-------------反序列化-------------");
//使用parseObject方法,并指定类,将JSON反序列化为一个指定的类对象
Object o3 = JSON.parseObject(JSON_Serialize,Person.class);
System.out.println(o3.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(o3);
}
}
|
运行结果
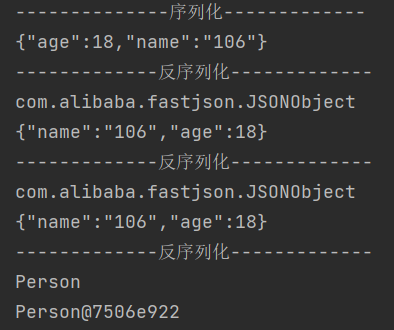
反序列化时不指定特定的类,那么Fastjosn就默认将一个JSON字符串反序列化为一个JSONObject。需要注意的是,对于类中private类型的属性值,Fastjson默认不会将其序列化和反序列化
1.2 @type参数
使用Fastjson中toJSONString进行序列化如果没有其他额外参数就会将将一个Java Bean转换成JSON字符串
1
2
3
4
| String JSON_Serialize = JSON.toJSONString(person);
System.out.println(JSON_Serialize);
//输出
//{"age":18,"name":"106"}
|
进行反序列化,JSON字符串反序列化成Java Object,可以使用parse()方法。该方法默认将JSON字符串反序列化为一个JSONObject对象。
1
2
3
4
5
| Object o1 = JSON.parse(JSON_Serialize);
System.out.println(o1.getClass().getName());
//com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject
System.out.println(o1);
//{"name":"Faster","age":18}
|
那么现在出现一个问题,如何将JSON字符串反序列化成我们原始的的类:有两个办法
- 添加SerializerFeature.WriteClassName属性
- 使用
parseObject()方法指定对象的类型
下面依次演示两种方法:
1.添加额外属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| String JSON_Serialize = JSON.toJSONString(person);
System.out.println(JSON_Serialize);
//{"age":18,"name":"106"}
//添加额外属性
String JSON_type = JSON.toJSONString(person, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName);
System.out.println(JSON_type);
//{"@type":"Person","age":18,"name":"106"}
|
对比不添加属性,发现JSON字符串中增加了一个@type字段,用于标识对象所属的类(1.2.25及之后的版本,禁用了部分autotype的功能)
1
2
3
4
| String JSON_str = "{\"@type\":\"Person\",\"age\":18,\"name\":\"106\"}";
System.out.println(JSON.parse(JSON_str));
//Person@6477463f
|
2.使用parseObject()方法指定对象的类型
1
2
3
4
5
| //使用parseObject方法,并指定类,将JSON反序列化为一个指定的类对象
Object o3 = JSON.parseObject(JSON_Serialize,Person.class);
System.out.println(o3);
//Person@3d71d552
|
1.3 执行过程
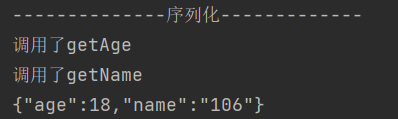
序列化:
使用toJSONString方法序列化时会自动调用get方法,其本质就是调用get方法获得对象属性,生成JSON字符串
反序列化:
1.指定@type为Person,使用parse方法
1
2
| String JSON_str = "{\"@type\":\"Person\",\"age\":18,\"name\":\"106\"}";
System.out.println(JSON.parse(JSON_str));
|
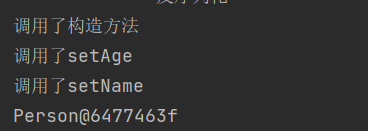
根据输出结果来看反序列化时先调用@type标识的类的构造函数,然后再调用set方法给对象赋值
2.指定@type为Person,使用parseObject方法
1
2
3
| String JSON_str = "{\"@type\":\"Person\",\"age\":18,\"name\":\"106\"}";
Object o3 = JSON.parseObject(JSON_str);
System.out.println(o3);
|
技巧
parseObject()只是对于parse()做了封装,判断返回的对象是否为JSONObject实例并强转为JSONObject类。
1
2
3
4
| public static JSONObject parseObject(String text) {
Object obj = parse(text);
return obj instanceof JSONObject ? (JSONObject)obj : (JSONObject)toJSON(obj);
}
|
根据结果可以看到返回了一个JSON Object对象,同时调用了构造方法、set、get方法,实际上是toJSON调用的get方法
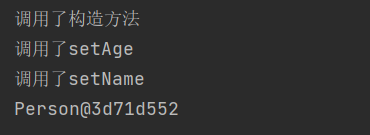
3.不使用@type,使用parseObject方法
调用了构造方法和set方法
1.4 反序列化过程
第一步:进入parse方法
1
2
3
4
| public static Object parse(String text) {
//调用了另一个方法重载
return parse(text, DEFAULT_PARSER_FEATURE);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public static Object parse(String text, int features) {
if (text == null) {
return null;
} else {
//创建并初始化DefaultJSONParer解析器
DefaultJSONParser parser = new DefaultJSONParser(text, ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance(), features);
Object value = parser.parse();
parser.handleResovleTask(value);
parser.close();
return value;
}
}
|
先跟进DefaultJSONParser,作用是对对输入的数据进行封装,在DefaultJSONParser中会对输入的json字符串进行判断如果开头是"{“给一个token值为12,如果是”[“给值14,在这里我们的token的值为12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public DefaultJSONParser(Object input, JSONLexer lexer, ParserConfig config) {
//此处省略一段代码
int ch = lexer.getCurrent();
if (ch == '{') {
lexer.next();
((JSONLexerBase)lexer).token = 12;
} else if (ch == '[') {
lexer.next();
((JSONLexerBase)lexer).token = 14;
} else {
lexer.nextToken();
}
}
|
返回之后紧接着进入DefaultJSONParser类中的parse方法Object value = parser.parse();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public Object parse(Object fieldName) {
//先将上一步DefaultJSONParser封装的结果赋值给lexer
JSONLexer lexer = this.lexer;
//会对token进行判断来执行不同的操作,Token值为12,创建了一个JSONObject对象
switch (lexer.token()) {
//省略若干行代码
case 12:
JSONObject object = new JSONObject(lexer.isEnabled(Feature.OrderedField));
return this.parseObject((Map)object, fieldName);
//省略若干行代码
}
}
|
接着跟进parseObject方法,161-170行对空白字符进行了过滤
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| while(true) {
lexer.skipWhitespace();
char ch = lexer.getCurrent();
if (lexer.isEnabled(Feature.AllowArbitraryCommas)) {
while(ch == ',') {
lexer.next();
lexer.skipWhitespace();
ch = lexer.getCurrent();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| if (key == JSON.DEFAULT_TYPE_KEY && !lexer.isEnabled(Feature.DisableSpecialKeyDetect)) {
//读取到类名
ref = lexer.scanSymbol(this.symbolTable, '"');
//用loadClass加载类
Class<?> clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(ref, this.config.getDefaultClassLoader());
|
进入loadClass方法,可以看到是有一些对字符的处理,这里可以作为我们黑名单绕过的一个利用点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
} else if (className.charAt(0) == '[') {
Class<?> componentType = loadClass(className.substring(1), classLoader);
return Array.newInstance(componentType, 0).getClass();
} else if (className.startsWith("L") && className.endsWith(";")) {
String newClassName = className.substring(1, className.length() - 1);
return loadClass(newClassName, classLoader);
|
加载返回类,并将类放入map中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| try {
ClassLoader contextClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (contextClassLoader != null) {
clazz = contextClassLoader.loadClass(className);
mappings.put(className, clazz);
return clazz;
}
} catch (Throwable var5) {
}
|
返回可以看到要根据class创建反序列化器,用反序列化器再去反序列化
1
2
3
4
| ObjectDeserializer deserializer = this.config.getDeserializer(clazz);
//用反序列化器去反序列化
thisObj = deserializer.deserialze(this, clazz, fieldName);
return thisObj;
|
跟进getDeserializer方法,根据判断条件,derializer为空,type为class执行进入getDeserializer((Class)type, type)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public ObjectDeserializer getDeserializer(Type type) {
ObjectDeserializer derializer = (ObjectDeserializer)this.derializers.get(type);
if (derializer != null) {
return derializer;
} else if (type instanceof Class) {
return this.getDeserializer((Class)type, type);
} else if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {
Type rawType = ((ParameterizedType)type).getRawType();
return rawType instanceof Class ? this.getDeserializer((Class)rawType, type) : this.getDeserializer(rawType);
} else {
return JavaObjectDeserializer.instance;
}
}
|
我们接着跟入getDeserializer重载方法,这里有黑名单,内容为java.lang.Thread
1
2
3
4
5
6
| for(int i = 0; i < this.denyList.length; ++i) {
String deny = this.denyList[i];
if (className.startsWith(deny)) {
throw new JSONException("parser deny : " + className);
}
}
|
没有匹配到对应的反序列化器,调用createJavaBeanDeserializer方法去创建
走进这个方法,我们前面快速步过,到这里走到了build,这个beanInfo保存了Person类里面的所有方法和一些变量以及构造方法
进入build方法,通过Java反射获取类的相关方法和成员变量字段,和无参构造方法
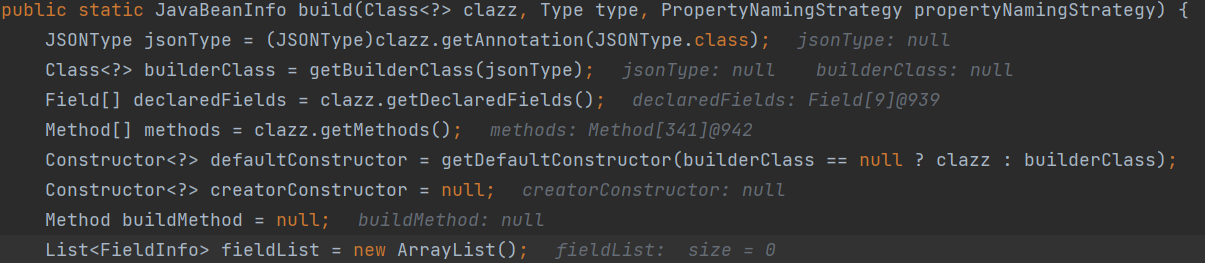
接着后面会对所有方法进行遍历找到符合要求的方法后续反序列化时自动调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| for(i = 0; i < var29; ++i) {
method = var30[i];
ordinal = 0;
int serialzeFeatures = 0;
parserFeatures = 0;
String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.length() >= 4 && !Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers()) && (method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE) || method.getReturnType().equals(method.getDeclaringClass()))) {
Class<?>[] types = method.getParameterTypes();
if (types.length == 1) {
annotation = (JSONField)method.getAnnotation(JSONField.class);
if (annotation == null) {
annotation = TypeUtils.getSuperMethodAnnotation(clazz, method);
}
if (annotation != null) {
if (!annotation.deserialize()) {
continue;
}
ordinal = annotation.ordinal();
serialzeFeatures = SerializerFeature.of(annotation.serialzeFeatures());
parserFeatures = Feature.of(annotation.parseFeatures());
if (annotation.name().length() != 0) {
methodName = annotation.name();
add(fieldList, new FieldInfo(methodName, method, (Field)null, clazz, type, ordinal, serialzeFeatures, parserFeatures, annotation, (JSONField)null, (String)null));
continue;
}
}
if (methodName.startsWith("set")) {
c3 = methodName.charAt(3);
String propertyName;
if (!Character.isUpperCase((char)c3) && c3 <= 512) {
if (c3 == 95) {
propertyName = methodName.substring(4);
} else if (c3 == 102) {
propertyName = methodName.substring(3);
} else {
if (methodName.length() < 5 || !Character.isUpperCase(methodName.charAt(4))) {
continue;
}
propertyName = TypeUtils.decapitalize(methodName.substring(3));
}
} else if (TypeUtils.compatibleWithJavaBean) {
propertyName = TypeUtils.decapitalize(methodName.substring(3));
} else {
propertyName = Character.toLowerCase(methodName.charAt(3)) + methodName.substring(4);
}
Field field = TypeUtils.getField(clazz, propertyName, declaredFields);
if (field == null && types[0] == Boolean.TYPE) {
isFieldName = "is" + Character.toUpperCase(propertyName.charAt(0)) + propertyName.substring(1);
field = TypeUtils.getField(clazz, isFieldName, declaredFields);
}
JSONField fieldAnnotation = null;
if (field != null) {
fieldAnnotation = (JSONField)field.getAnnotation(JSONField.class);
if (fieldAnnotation != null) {
if (!fieldAnnotation.deserialize()) {
continue;
}
ordinal = fieldAnnotation.ordinal();
serialzeFeatures = SerializerFeature.of(fieldAnnotation.serialzeFeatures());
parserFeatures = Feature.of(fieldAnnotation.parseFeatures());
if (fieldAnnotation.name().length() != 0) {
propertyName = fieldAnnotation.name();
add(fieldList, new FieldInfo(propertyName, method, field, clazz, type, ordinal, serialzeFeatures, parserFeatures, annotation, fieldAnnotation, (String)null));
continue;
}
}
}
if (propertyNamingStrategy != null) {
propertyName = propertyNamingStrategy.translate(propertyName);
}
add(fieldList, new FieldInfo(propertyName, method, field, clazz, type, ordinal, serialzeFeatures, parserFeatures, annotation, fieldAnnotation, (String)null));
}
}
}
}
|
根据上面代码可以看出,能够被调用的set方法要符合以下要求
- 方法名长度大于4
- 非静态方法
- 返回值为void或当前类
- 方法名以set开头
- 参数个数为1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| for(i = 0; i < var29; ++i) {
method = var30[i];
String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.length() >= 4 && !Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers()) && methodName.startsWith("get") && Character.isUpperCase(methodName.charAt(3)) && method.getParameterTypes().length == 0 && (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType()) || Map.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType()) || AtomicBoolean.class == method.getReturnType() || AtomicInteger.class == method.getReturnType() || AtomicLong.class == method.getReturnType())) {
JSONField annotation = (JSONField)method.getAnnotation(JSONField.class);
if (annotation == null || !annotation.deserialize()) {
String propertyName;
if (annotation != null && annotation.name().length() > 0) {
propertyName = annotation.name();
} else {
propertyName = Character.toLowerCase(methodName.charAt(3)) + methodName.substring(4);
}
fieldInfo = getField(fieldList, propertyName);
if (fieldInfo == null) {
if (propertyNamingStrategy != null) {
propertyName = propertyNamingStrategy.translate(propertyName);
}
add(fieldList, new FieldInfo(propertyName, method, (Field)null, clazz, type, 0, 0, 0, annotation, (JSONField)null, (String)null));
}
}
}
}
|
根据上面代码可以看出,能够被调用的get方法要符合以下要求
- 方法名长度大于等于4
- 非静态方法
- 以get开头且第4个字母为大写
- 无传入参数
- 返回值类型继承自Collection Map AtomicBoolean AtomicInteger AtomicLong
最后返回
1
| return new JavaBeanInfo(clazz, builderClass, defaultConstructor, (Constructor)null, (Method)null, buildMethod, jsonType, fieldList);
|
最后用反序列化器去反序列化
后面我们一直步过是看不见方法调试,因为后面是asm机制临时生成的代码在调试的时候是不可见的,直接继续往下调试,最后调用了set方法
asm机制:ASM是一个通用的Java字节码操作和分析框架。 它可以用于修改现有类或直接以二进制形式动态生成类
接着成功执行符合要求的方法和构造方法
2.fastjson反序列化漏洞
2.1 漏洞产生原因
根据上面的执行过程分析我们了解到反序列化时指定@type,parse和parseObject会调用相应类的get、set方法,这种autotype机制会导致如果在@type标识的类中的set或get方法存在恶意代码,那么就有可能导致fastjson反序列化漏洞。
2.2 利用链
2.2.1 Fastjson<=1.2.24
该版本下有两条利用链:JdbcRowSetImpl和Templateslmpl
JdbcRowSetImpl利用链
该利用链最终是结合JNDI注入来完成攻击过程,JDK版本限制和JNDI类似
调试分析
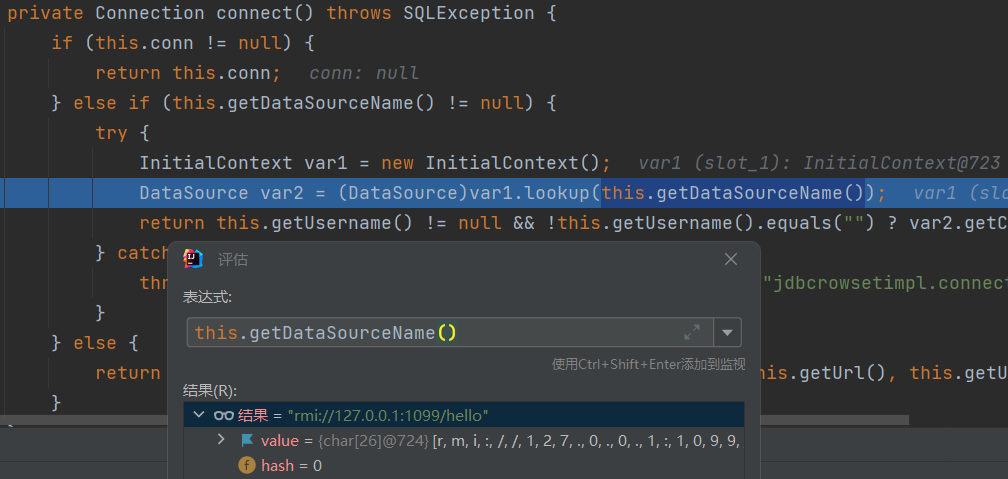
了解了具体的反序列过程和特性,我们可以现在JdbcRowSetImpl:setDataSourceName和setAutoCommit方法下断点
执行到setDataSourceName方法,可以看到var1是我们的playload中dataSourceName的值
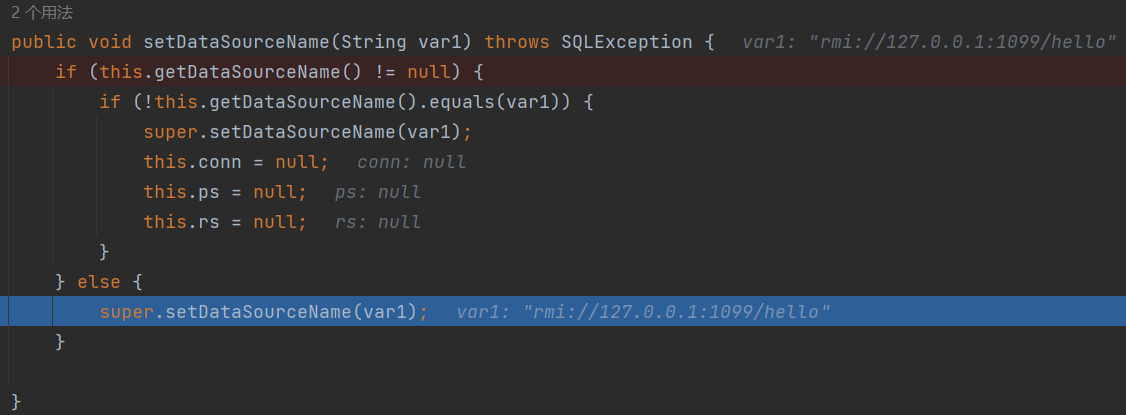
进入到父类的setDataSourceName方法,将name赋值给dataSource
autoCommit我们设置了值,所以这里就会进入connect方法
this.getDataSourceName()的返回值是我们传入的rmi地址这就造成了JDNI结合RMI的远程恶意代码执行
Templateslmpl链和高版本绕过在后续更新。。。